Introduction to AR and MA models
Contents
Introduction to AR and MA models¶
Time series models¶
aim to capture complex temporal dependence
build by combining processes with simple dependence structure - innovations
Innovations¶
white noise
martingale difference
iid
Linear time series models¶
The time series \(\mathbf{z}\) and the innovation \(\boldsymbol \varepsilon\) are linearly related
or more generally, the transformation \(\boldsymbol \varepsilon \rightarrow \mathbf{z}\) is affine
with Gaussian innovations \(p(\boldsymbol \varepsilon) \sim \mathcal{N}(\boldsymbol 0, \sigma^2\mathbf{I})\)
Moving Average (MA) models¶
MA(1)¶
Stationarity conditions¶
constant mean?
constant variance?
constant covariances?
for lag \(h=1\)
for lag \(h\geq 2\)
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", FutureWarning)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from statsmodels.tsa.arima_process import arma_acovf
from scipy.linalg import toeplitz
from matplotlib import rc
rc('font',**{'family':'serif','serif':['Palatino']})
rc('text', usetex=True)
plt.rcParams.update({'ytick.left' : True,
"xtick.bottom" : True,
"ytick.major.size": 0,
"ytick.major.width": 0,
"xtick.major.size": 0,
"xtick.major.width": 0,
"ytick.direction": 'in',
"xtick.direction": 'in',
'ytick.major.right': False,
'xtick.major.top': True,
'xtick.top': True,
'ytick.right': True,
'ytick.labelsize': 18,
'xtick.labelsize': 18
})
np.random.seed(12345)
def correlation_from_covariance(covariance):
v = np.sqrt(np.diag(covariance))
outer_v = np.outer(v, v)
correlation = covariance / outer_v
correlation[covariance == 0] = 0
return correlation
def show_covariance(cov_mat, process_name):
K = cov_mat.shape[0]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(20,8))
c = ax.imshow(cov_mat,
cmap="magma_r",
)
#c = ax.pcolormesh(Sigma, edgecolors='k', linewidth=.01, cmap='inferno_r')
#ax = plt.gca()
#ax.set_aspect('equal')
#ax.invert_yaxis()
plt.colorbar(c);
ax.set_xticks(range(0,K))
ax.set_xticklabels(range(1, K+1));
ax.set_yticks(range(0,K))
ax.set_yticklabels(range(1, K+1));
ax.set_title(f'Covariance {process_name}', fontsize=24)
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=-0.7)
n_obs = 20
arparams = np.array([0])
maparams = np.array([.4])
ar = np.r_[1, -arparams] # add zero-lag and negate
ma = np.r_[1, maparams] # add zero-lag
sigma2=np.array([1])
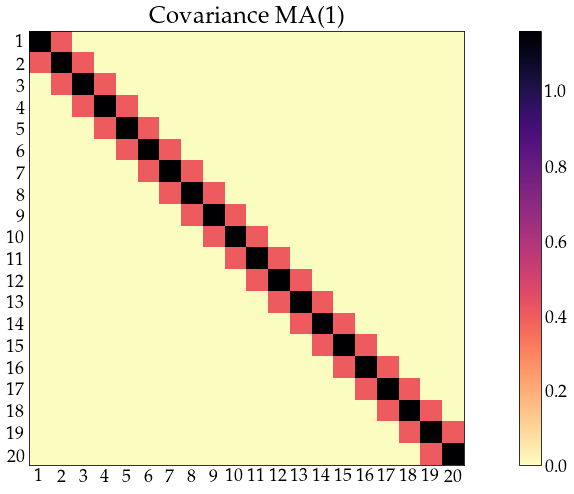
acov_ma1 = arma_acovf(ar=ar, ma=ma, nobs=n_obs, sigma2=sigma2)
Sigma_ma1 = toeplitz(acov_ma1)
corr_ma1 = correlation_from_covariance(Sigma_ma1)
show_covariance(cov_mat=Sigma_ma1, process_name='MA(1)')
n_obs = 20
arparams = np.array([0])
maparams = np.array([.4, .2])
ar = np.r_[1, -arparams] # add zero-lag and negate
ma = np.r_[1, maparams] # add zero-lag
sigma2=np.array([1])
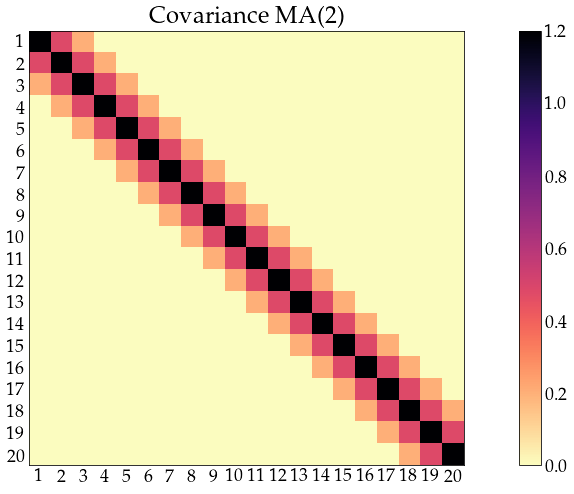
acov_ma2 = arma_acovf(ar=ar, ma=ma, nobs=n_obs, sigma2=sigma2)
Sigma_ma2 = toeplitz(acov_ma2)
corr_ma2 = correlation_from_covariance(Sigma_ma2)
show_covariance(cov_mat=Sigma_ma2, process_name='MA(2)')
need (at least) MA(q) to have dependence between \(z_t\) and \(z_{t+q}\)
not parsimonious (\(q+1\) parameters to estimate)
Autoregressive (AR) models¶
AR(1)¶
initial values \(z_0\)¶
known constant, e.g. \(z_0=0\)
unknown constant, to be estimated
unknown random variable, independent from \(\varepsilon_t\), e.g. \(z_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(0, \sigma^2_0)\), \(\sigma_0\) to be estimated
unknown random variable, independent from \(\varepsilon_t\) e.g. \(z_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(0, \frac{\sigma^2}{1-\alpha^2})\)
equivalent to \(z_0 = \frac{\varepsilon_0}{\sqrt{1-\alpha^2}}\), with \(\varepsilon_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(0, \sigma^2)\)
Stationarity conditions¶
constant variance (\(\sigma^2_{z_t} = \sigma^2_{z_{t+k}} = \gamma(0) \)):
since \(\sigma^2 > 0\), \(\alpha \neq \pm 1\)
constant mean (\(\operatorname E z_t = \operatorname E z_{t+k} = \mu_{z} \))
since \(\alpha \neq 1\)
constant covariances (\(\operatorname{cov}(z_t, z_{t+h}) = \operatorname E (z_t z_{t+h}) = \gamma(h)\))
covariance is time-invariant
correlation is time-invariant
(stability condition) for \(\operatorname{corr}(z_t, z_{t+h}) \rightarrow 0\) as \(h \rightarrow \infty\)
n_obs = 20
arparams = np.array([0.9])
maparams = np.array([0])
ar = np.r_[1, -arparams] # add zero-lag and negate
ma = np.r_[1, maparams] # add zero-lag
sigma2=np.array([1])
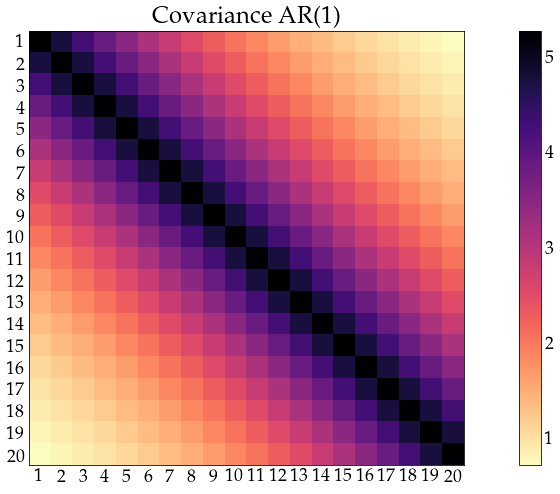
acov_ar1 = arma_acovf(ar=ar, ma=ma, nobs=n_obs, sigma2=sigma2)
Sigma_ar1 = toeplitz(acov_ar1)
corr_ar1 = correlation_from_covariance(Sigma_ar1)
show_covariance(cov_mat=Sigma_ar1, process_name='AR(1)')
MA and AR processes in Python¶
from statsmodels.tsa.arima_process import ArmaProcess
# create a MA(1) model
theta = np.array([.4])
ar = np.r_[1] # the coefficient on $z_t$
ma = np.r_[1, theta]
ma1_process = ArmaProcess(ar, ma)
print(ma1_process)
ArmaProcess
AR: [1.0]
MA: [1.0, 0.4]
autocovariances and autocorrelations (MA models)¶
ma1_process.acovf(3)
array([1.16, 0.4 , 0. ])
#compare to analytical result
print([1*(1+theta**2), theta])
[array([1.16]), array([0.4])]
def plot_autocov(process, nlags, process_name):
lags = np.arange(nlags+1)
acovf_x = process.acovf(nlags+1)
acf_x = process.acf(nlags+1)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(15, 4))
ax1.vlines(lags, [0], acovf_x, color='b')
ax1.scatter(lags, acovf_x, marker='o', c='b')
ax1.axhline(color='black', linewidth=.3)
ax1.set_xticks(lags)
ax1.set_xlabel('lags', fontsize=16)
ax1.set_ylabel('ACOVF', fontsize=16)
ax1.set_title(f'Theoretical autocovariances {process_name}', fontsize=20)
ax2.vlines(lags, [0], acf_x, color='b')
ax2.scatter(lags, acf_x, marker='o', c='b')
ax2.axhline(color='black', linewidth=.3)
ax2.set_xticks(lags)
ax2.set_xlabel('lags', fontsize=16)
ax2.set_ylabel('ACF', fontsize=16)
ax2.set_title(f'Theoretical autocorrelations {process_name}', fontsize=18)
def plot_sample(z, process_name):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,4))
ax.plot(z, c='black')
ax.set_xlabel('time', fontsize=16)
ax.set_title(f'{process_name}', fontsize=18)
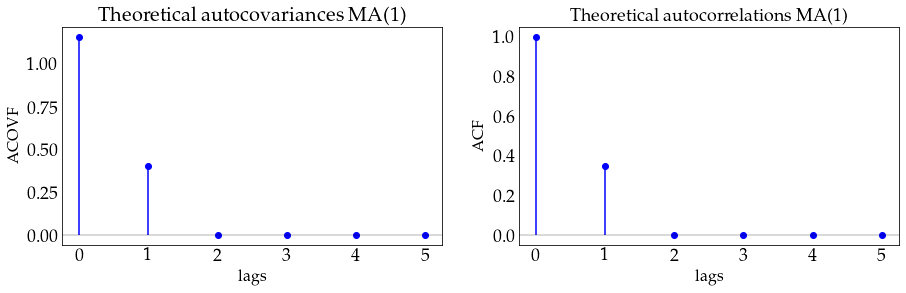
plot_autocov(process=ma1_process, nlags=5, process_name='MA(1)')
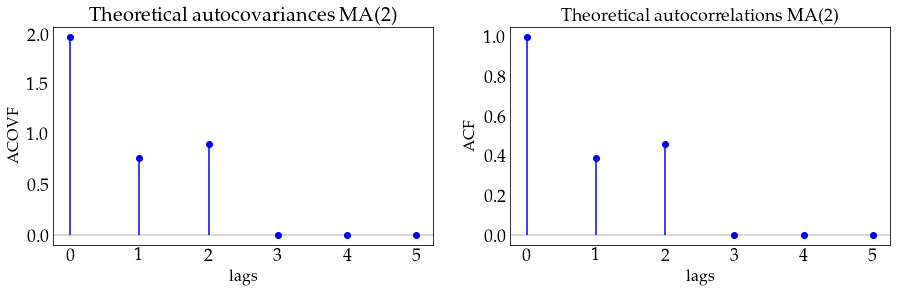
# define a MA(2) model
theta = np.array([.4, .9])
ar = np.r_[1] # the coefficient on $z_t$
ma = np.r_[1, theta]
ma2_process = ArmaProcess(ar, ma)
plot_autocov(process=ma2_process, nlags=5, process_name='MA(2)')
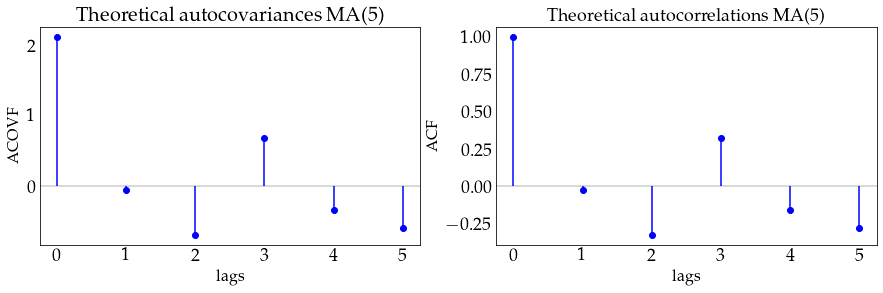
# define a MA(5) model
theta = np.array([.4, -.7, .3, -.1, -.6])
ar = np.r_[1] # the coefficient on $z_t$
ma = np.r_[1, theta]
ma5_process = ArmaProcess(ar, ma)
plot_autocov(process=ma5_process, nlags=5, process_name='MA(5)')
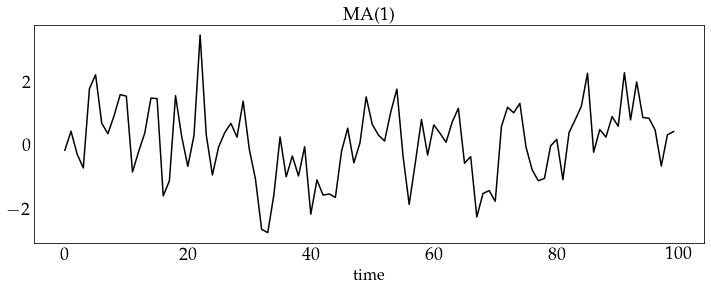
# generate a sample from the MA(1) model and plot it
z_ma1 = ma1_process.generate_sample(100)
plot_sample(z_ma1, process_name='MA(1)')
# generate a sample from the MA(2) model and plot it
z_ma2 = ma2_process.generate_sample(100)
plot_sample(z_ma2, process_name='MA(2)')
# generate a sample from the MA(5) model and plot it
z_ma5 = ma5_process.generate_sample(100)
plot_sample(z_ma5, process_name='MA(5)')
autocovariances and autocorrelations (AR models)¶
alpha = .8 # coefficient on z(t-1)
ar = np.r_[1, -alpha]
ma = np.r_[1] # coefficient on e(t)
ar1_process = ArmaProcess(ar, ma)
print(ar1_process)
ArmaProcess
AR: [1.0, -0.8]
MA: [1.0]
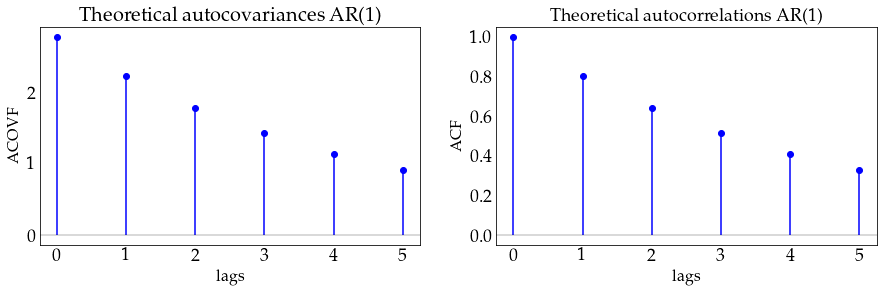
ar1_process.acovf(3)
array([2.77777778, 2.22222222, 1.77777778])
#compare to analytical result
sigma=1
print([sigma**2 / (1-alpha**2), \
alpha*sigma**2/(1-alpha**2), \
alpha**2*sigma**2/(1-alpha**2)
])
[2.7777777777777786, 2.222222222222223, 1.7777777777777788]
plot_autocov(process=ar1_process, nlags=5, process_name='AR(1)')
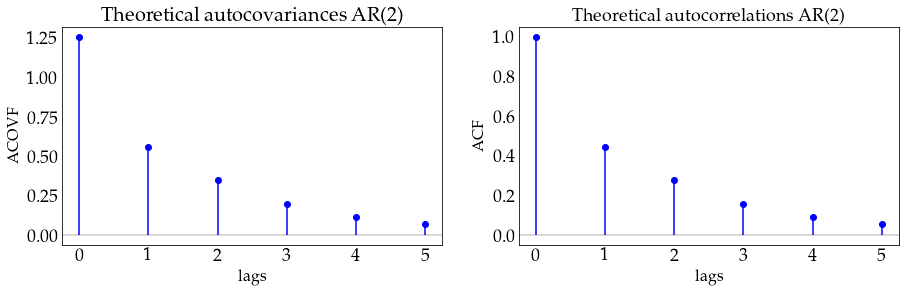
alpha = np.array([.4, .1])
ar = np.r_[1, -alpha] # the coefficient on $z_t$
ma = np.r_[1]
ar2_process = ArmaProcess(ar, ma)
plot_autocov(process=ar2_process, nlags=5, process_name='AR(2)')
alpha = np.array([.4, .2, -.3, .1, -.1])
ar = np.r_[1, -alpha] # the coefficient on $z_t$
ma = np.r_[1]
ar5_process = ArmaProcess(ar, ma)
plot_autocov(process=ar5_process, nlags=5, process_name='AR(5)')
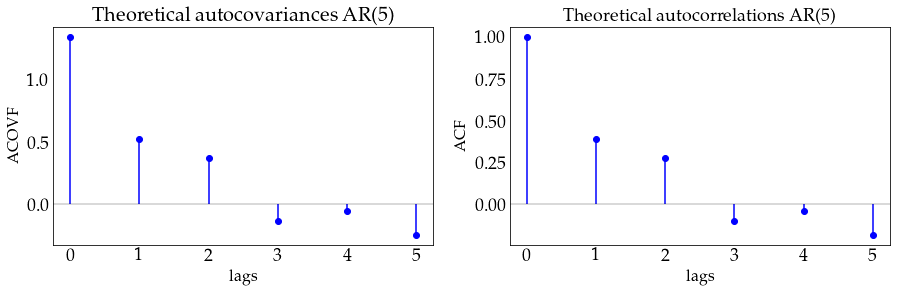
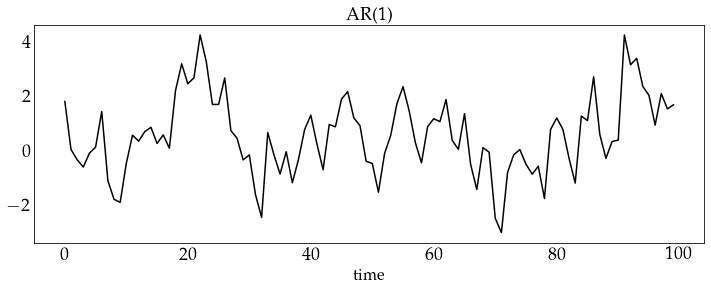
z_ar1 = ar1_process.generate_sample(100)
plot_sample(z_ar1, process_name='AR(1)')
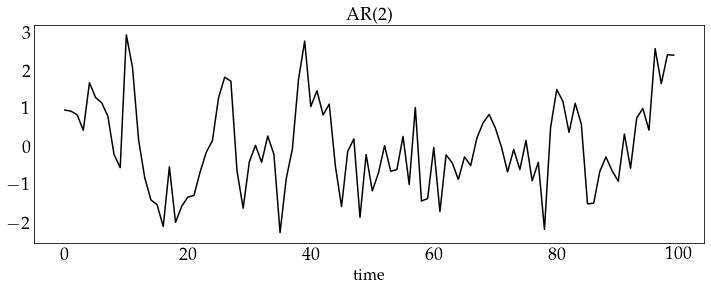
z_ar2 = ar2_process.generate_sample(100)
plot_sample(z_ar2, process_name='AR(2)')
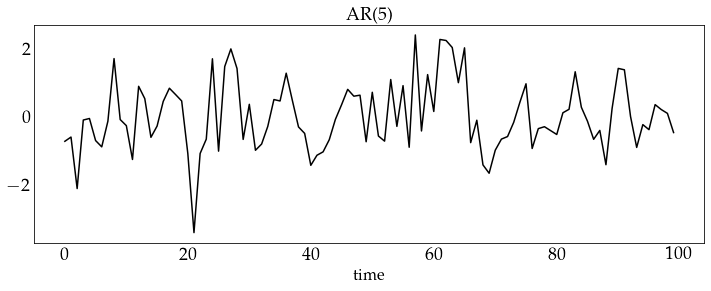
z_ar5 = ar5_process.generate_sample(100)
plot_sample(z_ar5, process_name='AR(5)')